The difference between the dispute of liability for damage to the interests of shareholders and the dispute of liability for damage to the interests of the company is analyzed and extended.
![]() Loading...
Loading...
![]() 2022.03.10
2022.03.10

There are 24 kinds of "company-related disputes" in Section 21 of Part VIII of the Notice of the Supreme People's Court on Issuing the Revised Provisions on the Cause of Action in Civil Cases (2020), of which disputes over liability for damaging the interests of shareholders and disputes over liability for damaging the interests of the company are separated. In practice, when a shareholder files a lawsuit to safeguard the relevant rights, the cause of the lawsuit needs to be considered based on different factors such as the purpose of the lawsuit, the difficulty of proof, and the specific legal relationship. There is some confusion between the dispute of liability for damage to the interests of shareholders and the dispute of liability for damage to the interests of the company, so this paper will analyze the differences between the two cases, and explore the relevant issues derived from the two cases.
1. The main differences between the two
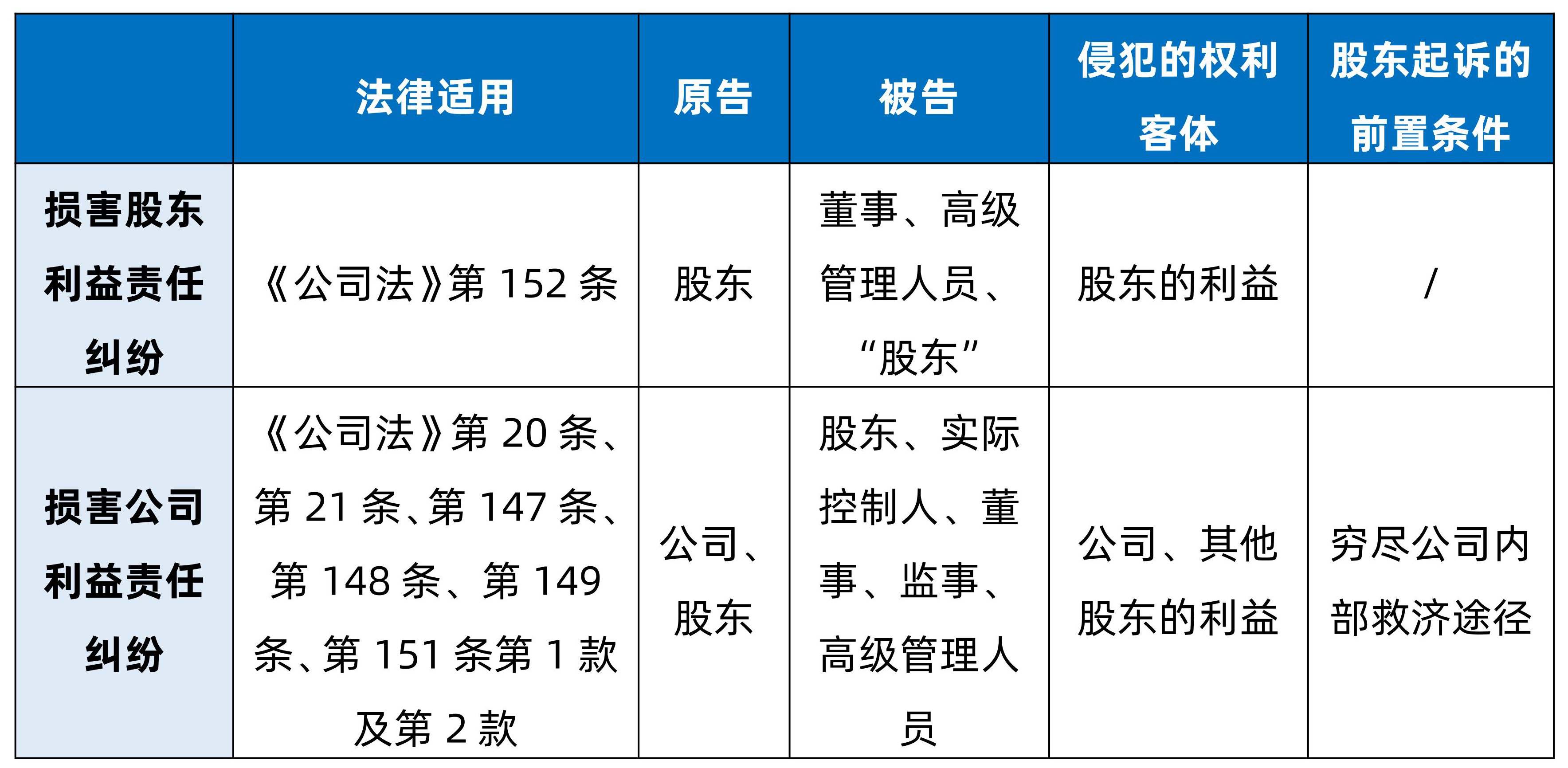
1.The application of law in disputes over liability for damage to the interests of shareholders.
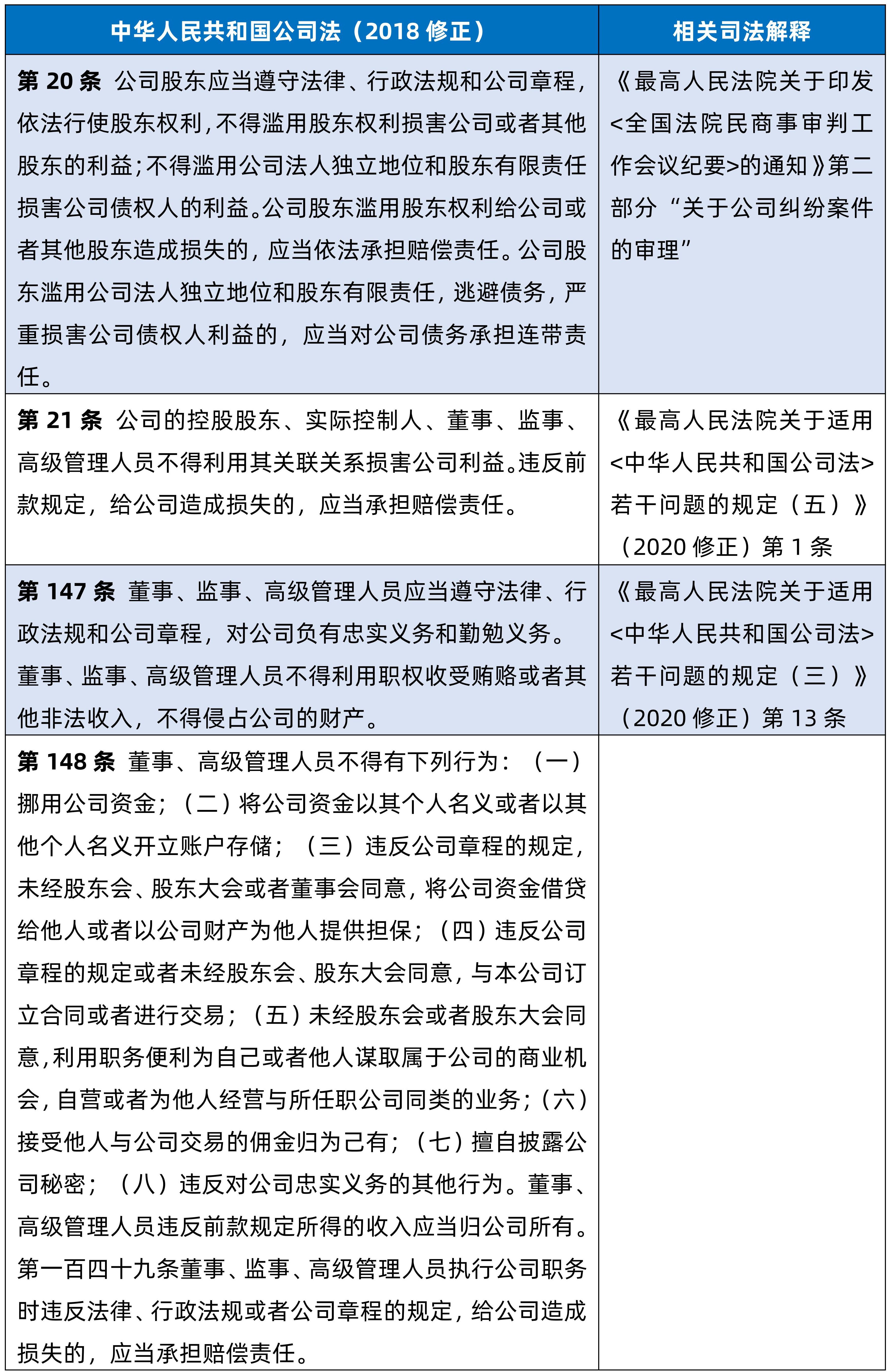
The main legal basis is Article 152 of the the People's Republic of China Company Law: "If a director or senior manager violates the provisions of laws, administrative regulations or the articles of association and harms the interests of shareholders, the shareholders may bring a lawsuit in the people's court".
The relevant judicial interpretation involved is Article 5 of the "Several Provisions of the Supreme People's Court on the Trial of Civil Compensation Cases for Infringement of False Statements in the Securities Market". "Failure to disclose information in accordance with regulations" as stipulated in Article 85 of the Securities Law refers to information disclosure obligations. The person fails to disclose information in a timely and fair manner in accordance with the prescribed time limit and method. If the information disclosure obligor's failure to disclose information in accordance with the regulations constitutes a false statement, it shall bear civil liability in accordance with these provisions; if it constitutes insider trading, it shall bear civil liability in accordance with the provisions of Article 53 of the Securities Law; if it constitutes an act of harming the interests of shareholders as stipulated in Article 152 of the Company Law, it shall bear civil liability in accordance with the law ".
2.The application of the law in disputes over liability for damage to the interests of the company.

1.The meaning of the dispute of liability for damage to the interests of shareholders lies in the protection of the right of the shareholders of the company to sue directly, which can only be brought by the shareholders.(1)The shareholders of the company may directly file a lawsuit with the court if the directors or executives violate the laws, administrative regulations or the articles of association to damage their rights.
2.The plaintiff in a dispute over liability for damage to the interests of the company may be the company or a shareholder. According to the provisions of Articles 23 and 24 of the (IV) of the Supreme People's Court on Several Issues Concerning the Application of the the People's Republic of China Company Law, the board of supervisors or the supervisors of a limited liability company without a board of supervisors, the board of directors or the executive directors of a limited liability company without a board of directors If a lawsuit is filed against a director, senior manager or supervisor in accordance with Article 151 of the "Company Law", the company shall be listed as the plaintiff. However, unlike disputes over liability for damage to the interests of shareholders, if shareholders act as plaintiffs to sue on the grounds of disputes over liability for damage to the interests of the company, they should first exhaust the internal remedies of the company, and the internal organs of the company should bring a lawsuit to the court. In addition, Article 4 of the "Decision of the Supreme People's Court on Amending the Provisions on Several Issues Concerning the Application of the the People's Republic of China Company Law" "The period of continuous shareholding for more than 180 days stipulated in Article 151 of the Company Law shall be the period of shareholding that has expired when shareholders file a lawsuit with the people's court; the prescribed total holding of more than 1% shares of the company refers to the total holding of more than two shareholders' shares", making further provisions on the identity of shareholders.
1.Defendants in disputes over liability for damage to the interests of shareholders are directors and senior management. Opinions on whether shareholders can become defendants are different in various courts. In (2015) Minshen Zi No. 3353 case, the Supreme Court held that the basis of the four plaintiffs' claim in the original trial was Article 152 of the Company Law, and the defendant was not a director or executive of the company, so the original trial found that the defendant was not a qualified defendant in the case of liability for damaging the interests of shareholders and applied the law is not improper;;(2)In the case of (2018) Jingmin Shen No. 4724, the Beijing High Court supported the plaintiff's claim that the defendant, as a shareholder, should be liable for compensation.(3)
2.The defendant in a dispute over liability for damage to the interests of the company may be a shareholder, actual controller, director, supervisor or senior manager of the company, but if the infringement or breach of contract of a third party harms the interests of the company, it does not belong to the cause of the case. In practice, the examination of the identity of senior executives is mainly based on whether they have assumed corresponding responsibilities in the daily operation and management of the company, while the identification of the actual controller is mainly based on the company's industrial and commercial registration information, articles of association, internal resolutions or other agreements and other factors.

(IV) Different objects of rights infringed(4)
1.A dispute over liability for damage to the interests of shareholders is a dispute arising from the violation of laws, administrative regulations or the articles of association by directors and senior managers to the detriment of the interests of shareholders, and the object of infringement is the rights of shareholders.
2.Damage to the interests of the company liability dispute is the company as a party whose interests are damaged, the company's shareholders, the actual controller of the abuse of shareholders' rights or directors, supervisors, senior managers in violation of statutory obligations, the company's articles of association, damage the rights of the company.
2. Discussion on the Extension of the Two Cases
(I) Whether dormant shareholders can directly bring a lawsuit against the company.
The shareholders referred to above generally refer to the nominal shareholders recorded in the register of shareholders, the articles of association of the company and registered with the company registration authority, as to whether the "hidden shareholders" as the actual funder can directly bring up a dispute over liability for damage to the interests of shareholders or shareholder subrogation, generally speaking, the hidden shareholders need to be named before the filing. In Shenzhen, for example, there are two cases of disputes over liability for the benefit of dormant shareholders as of February 11, 2022, retrieved through the China Judgment Documents Network.
In (2019) Guangdong 0303 Minchu No. 32997 case, the court held that the plaintiff Xiao Jinping did not have the subject qualification to sue the defendants Liu Weiqiang and Pan Yin in accordance with the provisions of Article 20 of the the People's Republic of China Company Law. Therefore, the lawsuit filed in this case did not conform to the civil procedure stipulated in the Civil Procedure Law and was rejected.(5)
In addition, in the case of (2020) Yue 0391 Minchu No. 346, the court found that Li Wanlin filed a lawsuit against Zhu Jianfei in 2018, requesting to terminate the equity transfer agreement between him and Zhu Jianfei. The request was ultimately not supported by the people's court. In this case, the court held that the Equity Transfer Agreement signed between Li Wanlin and Zhu Jianfei did not violate the law and was legal and effective, li Wanlin's name is not recorded in the company's register of shareholders, it is not convenient to directly exercise the company's shareholder rights, for Li Wanlin's transfer of 10% of the equity, Zhu Jianfei is a nominal shareholder, in the exercise and disposition of the 10% of the equity should obtain Li Wanlin's consent. The two defendants decided to dissolve the company without Li Wanlin's participation, and they also had sufficient reasons to prove to Li Wanlin that the company should be dissolved. It is obvious that the plaintiff's above-mentioned rights have not been protected, so the plaintiff should not bear the burden of proof for the loss involved, and finally the court supported the plaintiff Li Wanlin's claim.(6)

Since the anonymous shareholders have not registered for publicity, according to the principle of commercial appearance, there is no antagonistic effect to the outside world, and if the anonymous shareholders file a direct dispute over liability for damage to the interests of shareholders or a lawsuit of shareholder subrogation, they need to confirm their identity as shareholders first. However, in the event of a dispute, it is often difficult for the hidden shareholders to obtain the cooperation of the nominal shareholders or directly with the consent of more than half of the other shareholders of the company, and it is necessary to obtain the qualification of the plaintiff by filing a lawsuit for the confirmation of shareholder qualification before filing the relevant lawsuit.
(II) Jurisdiction under both cases
1.Damage to the interests of shareholders Liability disputes
Since the damage to the interests of shareholders is a general tort, the provisions of Article 29 of the the People's Republic of China Civil Procedure Law and Article 24 of the Interpretation of the Supreme People's Court on the Application of the the People's Republic of China Civil Procedure Law shall apply. The Beijing High Court held in (2021) Jingmin Jurisdiction Final No. 212 that "Article 28 of the the People's Republic of China Civil Procedure Law stipulates that a lawsuit brought by a tort shall be under the jurisdiction of the people's court of the place where the tort is committed or where the defendant is domiciled. This case is a dispute over liability for damage to the interests of shareholders and belongs to a lawsuit brought by a tort, and the people's court of the place where the tort or the defendant is domicile has jurisdiction over the case". (7) Therefore, after the interests of the shareholders of the company have been infringed, the shareholders of the company may, from the place of infringement (including the place where the infringement was committed and the place where the result of the infringement occurred) and the court of the defendant's domicile, choose one of them to bring a lawsuit for liability for damage to the interests of shareholders.
2.Damage to the interests of the company liability disputes

Article 27 of the Company Law provides for the special territorial jurisdiction of disputes over the interests of the company, and the general application of the special jurisdiction of the company to the establishment of the company, the confirmation of the qualification of shareholders, the distribution of profits, dissolution, etc. And does "etc." here mean that all types of corporate litigation apply?
The Supreme People's Court held in (2017) the Supreme People's Court case No. 391 that "this case is a dispute over liability for damaging the interests of the company. According to the "Provisions on Causes of Action in Civil Cases" (amended for the first time according to (Law [2011] No. 41)), disputes over liability for damaging the interests of the company have been expressly included in the 256th cause of action of Part VIII bis 11 "Disputes Related to the Company" of the provisions, and are not included in the "Tort Liability Disputes" of Part IX of the provisions. As the trial of this case may involve the collection and retrieval of evidence related to the interests of the company, the examination of the necessity and legality of the shareholder representative litigation, etc., it is appropriate that the case be under the jurisdiction of the people's court of the company's domicile, so as to facilitate the litigation of the parties and the people's court to hear the case in accordance with the law."(8)
However, in the case No. 325 of the Supreme People's Court of the Supreme People's Court (2019), the court held that "the company filed a lawsuit on the grounds that specific directors and shareholders harmed the interests of the company, which is not in line with the characteristics that the company organization lawsuit involves multiple lawsuits on the same organization law behavior of the same company, or there are multiple legal relationship changes of most interested parties related to the company organization, the general provisions of the territorial jurisdiction of the Civil Procedure Law should be applied rather than the special territorial jurisdiction provisions. A lawsuit that belongs to the traditional sense of infringement should not be subject to special territorial jurisdiction, but the principle of jurisdiction over general tort disputes should be applied".(9)Accordingly, the dispute over liability for damage to the interests of the company does not of course apply the provisions of Article 27 of the Civil Procedure Law, from the above-mentioned part of the Supreme Court's decision point of view, the implementation of the principle of special territorial jurisdiction of the case type is characterized by the object of the lawsuit is the legal relationship of the nature of the company's organic law, the effect of the judgment and the company.(10)
Therefore, if a lawsuit is filed on the grounds of a dispute over liability for damage to the interests of the company, it is necessary to analyze the specific case, and to determine whether Article 27 or Article 29 of the Civil Procedure Law is applicable in terms of the nature of the case organization, the identification of the parties, the attribution of the interests of winning the case, etc., in combination with the court's decision tendency.
(III) The relationship between the dispute of liability for damage to the interests of the company and the dispute of liability for damage to the company's related transactions.
The dispute of liability for damage to the interests of the company includes the dispute of liability for damage to the company's related transactions, the former is the general situation, the latter is the special situation. Related party transaction damage liability disputes are common in the daily business activities of listed companies. They mainly occur when the company's controlling shareholders, actual controllers, directors, supervisors and other related parties use related relationships to harm the company's interests. Article 21 of the Company Law and Article 216, Item 4 of the Company Law "The meaning of the following terms in this law: (4) Related relationship, refers to the relationship between the company's controlling shareholders, actual controllers, directors, supervisors, and senior managers and the enterprises directly or indirectly controlled by them, as well as other relationships that may lead to the transfer of the company's interests. However, enterprises controlled by the state not only have an associated relationship because they are controlled by the state", and Article 84 of the the People's Republic of China Civil Code "controlling investors, actual controllers, directors, supervisors and senior managers of profit-making legal persons shall not use their associated relationship to damage the interests of legal persons; if they cause losses to legal persons by using the associated relationship, they shall be liable for compensation."
According to the definition of related party transactions in Item 4 of Article 216 of the Company Law, when a party files a lawsuit on the grounds of a company's related party transaction damage liability dispute, it needs to bear a higher burden of proof than the company's interest liability dispute, that is, it needs to further prove that the defendant has related party transactions, and there is an associated relationship between the transfer of the company's interests and the enterprise directly or indirectly controlled by the defendant. If it cannot be proved that it is in the form of a related transaction, it is appropriate to sue on the grounds of a liability dispute that harms the interests of the company.
3. Epilogue
The analysis and understanding of the differences between the different cases in the company dispute will help the attorney to better grasp the choice of the case and formulate the litigation strategy according to the specific circumstances of the case, including the principal's ability to prove the evidence, the identification of shareholders and so on.
References:
(1) See Xi Xiaoming: "Understanding and Application of the Provisions on the Cause of Action of Civil Cases of the Supreme People's Court" (revised edition in 2011), People's Court Press, 2011 edition, pp. 392-393.
(2) See the Supreme People's Court (2015) Min Shen Zi No. 3353 Su Maoqian, Zhou Zhenyou, etc. and Chen Bin, Zheng Yicheng to damage the interests of shareholders liability dispute appeal, application for civil ruling, judgment date December 28, 2015.
(3) See Beijing Higher People's Court (2018) Jing Min Shen No. 4724 Xu Shengfa and Beijing Huasheng Jing Technology Co., Ltd. and other civil rulings on retrial review and trial supervision, with the judgment date of December 27, 2018.
(4) See Li Sen: "Research on Issues Related to Disputes over Liability for Damage to the Interests of Companies", Nanshan District People's Court of Shenzhen City, released on October 20, 2016.
(5) See Shenzhen Luohu District People's Court (2019) Guangdong 0303 Minchu No. 32997 Xiao Jinping and Liu Weiqiang, Pan Yin damage to the interests of shareholders liability dispute first instance civil ruling, decision date September 24, 2020.
(6) See Shenzhen Qianhai Cooperation Zone People's Court (2020) Guangdong 0391 Minchu No. 346 Li Wanlin and Zhu Jianfei and Lu Meiyou Civil Judgment of First Instance in Dispute over Liability for Damage to Shareholders' Interests, Decision Date April 29, 2020.
(7) See Beijing Higher People's Court (2021) Beijing People's Court No. 212 Beijing Xinhua Guotai Water Conservancy Asset Management Co., Ltd. and Qu He Investment Group Co., Ltd. in the civil ruling on the dispute over liability for damaging the interests of shareholders, the ruling date is October 29, 2021.
(8) See the Supreme People's Court (2017) Supreme Law Civil Jurisdiction Final No. 391 Hengfu Venture Capital Enterprise and Lixun Investment (Hong Kong) Co., Ltd. for the second instance civil ruling on the dispute over liability for damaging the company's interests, the ruling date is November 30, 2017.
(9) See the Supreme People's Court (2019) Supreme Law Civil Jurisdiction Final 325 Tan Guoren, Yunnan Yongbao Special Cement Co., Ltd. damage to the interests of the company liability dispute second instance civil ruling, the decision date of July 29, 2019.
(10) See Wuhu Economic and Technological Development Zone People's Court: "Jurisdiction Principles for Disputes over Damage Liability for Related Party Transactions of Companies", published on the People's Court Network of Wuhu Economic and Technological Development Zone, June 27, 2016.





